Precision CNC Turning: Accuracy in Machining
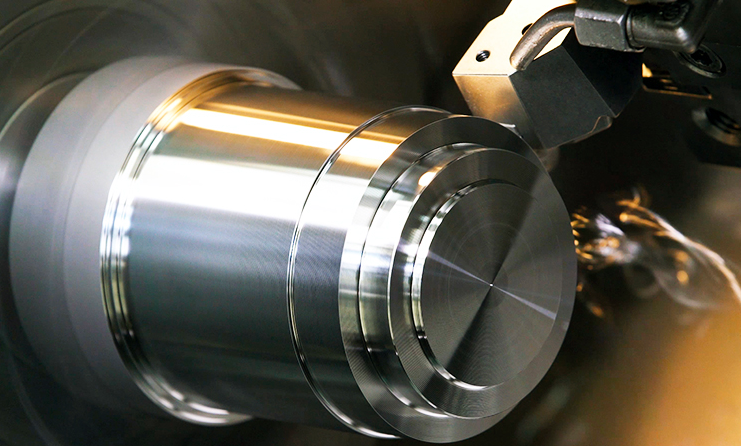

In the world of modern manufacturing, precision CNC turning plays a crucial role in producing highly accurate components. Industries that demand tight tolerances and superior surface finishes, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics, rely heavily on CNC turning to ensure quality and efficiency.
This article explores precision CNC turning, how it works, its advantages, applications, and what makes it an essential part of today’s industrial landscape.
Understanding Precision CNC Turning
Precision CNC turning is a subtractive machining process where a cylindrical workpiece rotates at high speeds while a cutting tool removes excess material to achieve the desired shape. Unlike traditional turning methods, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning operates with extreme accuracy, guided by programmed instructions that eliminate human error.
This process ensures repeatability, high precision, and efficiency, making it ideal for both prototyping and large-scale production. The ability to work with a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, further enhances its versatility.
How Precision CNC Turning Works
1. Design and Programming
The first step involves creating a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model of the part. This design is then converted into G-code, which serves as the machine’s instructions for cutting and shaping the material.
2. Material Selection
The choice of material depends on the application. Common materials used in precision CNC turninginclude:
- Metals: Aluminum, stainless steel, brass, titanium
- Plastics: Nylon, PEEK, polycarbonate
- Composites: Carbon fiber, fiberglass
3. Workpiece Setup
The selected material is clamped securely in the lathe’s chuck or collet to prevent movement during machining.
4. Turning Operations
The CNC lathe rotates the workpiece at high speeds, while the cutting tool removes material according to the programmed design. Several operations can be performed, including:
- Facing: Flattening the end of the workpiece
- Tapering: Creating a gradual reduction in diameter
- Threading: Cutting screw threads
- Grooving: Creating precise channels or recesses
5. Quality Inspection
After machining, the finished part undergoes dimensional checks and surface inspections to ensure compliance with specifications.
Key Advantages of Precision CNC Turning
Precision CNC turning offers multiple benefits that make it superior to traditional machining methods.
1. Exceptional Accuracy
CNC turning achieves tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches, ensuring that each part meets exact specifications.
2. High Efficiency and Speed
With automated controls and continuous operation, CNC turning significantly reduces production time.
3. Cost-Effective for Large Runs
The repeatability of CNC turning makes it ideal for mass production, reducing waste and labor costs.
4. Complex Geometries and Fine Details
Precision CNC turning allows for intricate shapes, internal features, and fine surface finishes that would be challenging with manual methods.
5. Versatile Material Compatibility
From soft plastics to hardened steels, CNC turning can handle a wide range of materials without compromising quality.
6. Consistency and Repeatability
CNC programming ensures that every part produced is identical, making it perfect for industries requiring uniformity and reliability.
Applications of Precision CNC Turning
Precision CNC turning is used across various industries due to its ability to produce high-quality, durable components.
1. Aerospace Engineering
Aircraft and spacecraft manufacturers require high-precision components such as turbine shafts, landing gear parts, and fasteners.
2. Automotive Industry
CNC-turned parts like axles, brake components, and fuel system parts are essential for vehicle performance and safety.
3. Medical Sector
The medical industry uses CNC turning for surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and prosthetics that meet strict health standards.
4. Electronics and Telecommunications
Connectors, heat sinks, and casings for electronic devices rely on CNC turning for precision and reliability.
5. Industrial Machinery
CNC turning produces custom gears, rollers, and machine tool components used in heavy-duty industrial applications.
6. Defense and Military
The defense sector uses precision CNC turning for weapon parts, armored vehicle components, and durable hardware.
Precision CNC Turning vs. CNC Milling
Though both CNC turning and CNC milling are widely used, they serve different purposes.
| Feature | Precision CNC Turning | CNC Milling |
| Workpiece Movement | Rotates on a spindle | Remains stationary |
| Cutting Tool Movement | Stationary or limited movement | Moves in multiple directions |
| Best for | Cylindrical and symmetrical parts | Complex 3D shapes and flat surfaces |
| Production Speed | Faster for round parts | Slower for intricate geometries |
| Cost | More cost-effective for cylindrical parts | Higher cost for detailed parts |
Choosing a Precision CNC Turning Service
Selecting the right CNC turning service provider is essential for ensuring quality and efficiency. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Experience and Expertise
A provider with years of experience in precision CNC turning will likely deliver better results.
2. Advanced Machinery
Look for companies that use state-of-the-art CNC lathes with multi-axis capabilities for more complex designs.
3. Material Options
A reliable provider should offer a wide selection of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
4. Quality Assurance
Ensure the provider follows strict quality control standards and has certifications like ISO 9001.
5. Lead Time and Cost
Compare turnaround times and pricing to get the best balance between quality and affordability.
6. Customization and Support
A good CNC turning service should provide custom machining solutions and responsive customer service.
Future Trends in Precision CNC Turning
Technology advancements are continuously improving CNC turning, making it faster, smarter, and more efficient.
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence is helping optimize tool paths, reduce errors, and improve efficiency.
2. Smart Automation
New CNC lathes come with robotic loading and real-time monitoring, increasing productivity and reducing downtime.
3. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Machining
Manufacturers are adopting energy-efficient CNC machines and sustainable materials to reduce environmental impact.
4. Hybrid Manufacturing
The combination of CNC turning and additive manufacturing (3D printing) is unlocking new possibilities for complex designs.
5. Digital Twin Technology
Using digital simulations of CNC turning operations allows manufacturers to optimize machining processes before production.
Conclusion
Precision CNC turning is a vital machining process that ensures high-quality, accurate, and efficient production of cylindrical components. Its ability to handle tight tolerances, complex geometries, and a variety of materials makes it a preferred choice in many industries.
With continuous advancements in AI, automation, and sustainable machining, the future of CNC turning looks promising. Whether for prototyping, small-batch production, or mass manufacturing, CNC turning remains a cornerstone of precision engineering, delivering reliability and excellence in every component.